Floating caused by the phenomenon of ground effect – Floating, caused by the phenomenon of ground effect, is an intriguing phenomenon where vehicles or objects hover above the ground or water due to the interaction between their shape and the surrounding air or fluid. This article delves into the principles, applications, and future prospects of floating technology, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance in various industries.
Ground effect occurs when a vehicle or object moves close to a surface, creating a cushion of air or fluid beneath it. This cushion reduces drag and increases lift, enabling the vehicle or object to float. Understanding the physics behind floating is crucial for designing and operating floating vehicles effectively.
Introduction to Ground Effect: Floating Caused By The Phenomenon Of Ground Effect
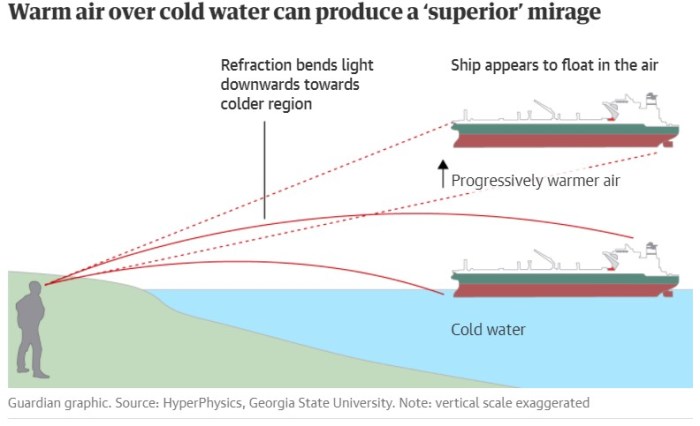
Ground effect is an aerodynamic phenomenon that occurs when a vehicle or object moves close to the ground or a surface. It is characterized by a reduction in drag and an increase in lift, resulting in improved efficiency and performance.
Ground effect requires specific conditions to occur, including a smooth and level surface, a vehicle with a low ground clearance, and a sufficient speed. It is commonly observed in vehicles such as racing cars, hovercrafts, and aircraft during takeoff and landing.
Physics of Floating
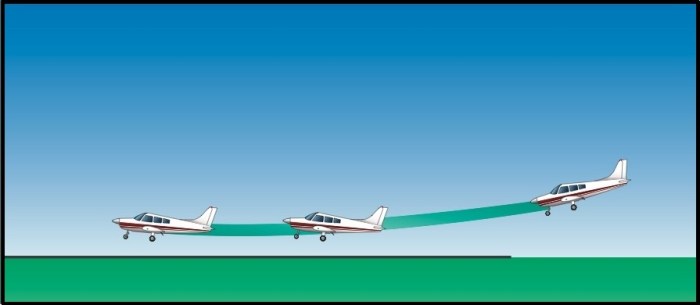
Floating is a state in which an object is suspended in a fluid, such as air or water, without sinking. It is achieved through a combination of aerodynamic forces, including lift and buoyancy.
Lift is generated by the pressure differential created around a vehicle as it moves through a fluid. The shape of the vehicle, particularly its wings or foils, is designed to create a region of low pressure above and a region of high pressure below, resulting in an upward force.
Buoyancy is the upward force exerted by a fluid on an object immersed in it. In the case of floating vehicles, buoyancy is provided by the air or water displaced by the vehicle’s volume.
Applications of Floating
Floating technology has found applications in various industries, including:
- Transportation:Hovercrafts, ground-effect vehicles (GEVs), and ekranoplans utilize ground effect to achieve high speeds and efficient movement over water or land.
- Military:Stealth aircraft and missiles employ ground effect to reduce radar signature and improve maneuverability.
- Entertainment:Hoverboards and jetpacks provide recreational experiences based on floating principles.
Design Considerations for Floating Vehicles, Floating caused by the phenomenon of ground effect
The design of floating vehicles involves balancing factors such as weight, buoyancy, and stability.
Weight:The weight of the vehicle must be kept low to maintain buoyancy. Lightweight materials, such as composites and carbon fiber, are commonly used.
Buoyancy:The shape and volume of the vehicle determine its buoyancy. A larger surface area and a streamlined shape increase buoyancy.
Stability:Floating vehicles must be designed to maintain stability in various conditions. This can be achieved through proper weight distribution, control systems, and aerodynamic design.
Challenges and Future of Floating Technology
Current challenges in floating technology include:
- Energy efficiency:Floating vehicles require significant power to overcome drag and maintain lift.
- Control systems:Advanced control systems are needed to ensure stability and maneuverability in various conditions.
- Safety regulations:The development and deployment of floating vehicles require clear safety regulations and standards.
Future advancements in materials, propulsion, and control systems are expected to address these challenges and expand the applications of floating technology.
General Inquiries
What is the key principle behind floating caused by ground effect?
The principle is based on the generation of a pressure differential between the upper and lower surfaces of the vehicle or object, creating lift that counteracts gravity.
What are the advantages of floating vehicles?
Floating vehicles offer reduced drag, increased lift, enhanced maneuverability, and the ability to traverse challenging terrains.
What are the challenges in floating technology?
Challenges include maintaining stability, developing efficient propulsion systems, and addressing control issues.
