Who is responsible for the sizing of product backlog items – In the realm of agile development, the sizing of product backlog items holds immense significance, directly impacting project outcomes. This discourse delves into the intricate web of responsibilities, best practices, and tools involved in determining the appropriate size for these crucial elements, providing a comprehensive guide for stakeholders seeking to optimize their agile processes.
Who is Responsible for the Sizing of Product Backlog Items?
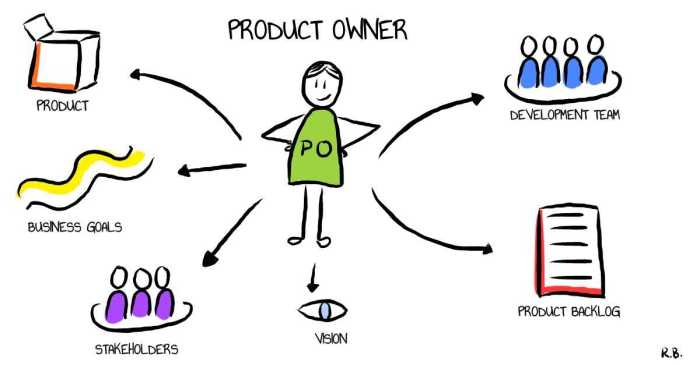
Determining the appropriate size of product backlog items is a crucial aspect of agile development. The responsibility for this task is shared among the Product Owner, Development Team, and Scrum Master, each playing a distinct role in the process.
Product Owner’s Responsibilities, Who is responsible for the sizing of product backlog items
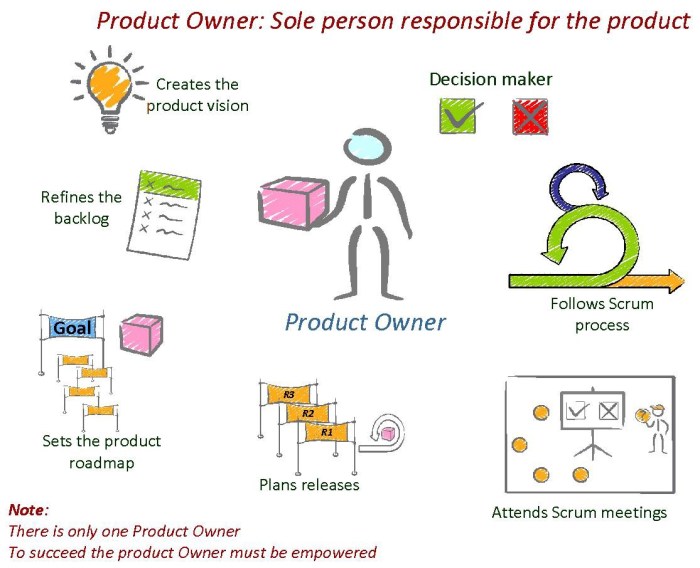
The Product Owner holds primary responsibility for defining and prioritizing backlog items. They play a significant role in influencing item size by:
- Defining clear and concise user stories that articulate the desired functionality.
- Breaking down large or complex stories into smaller, more manageable chunks.
- Setting realistic expectations for the Development Team regarding the scope and complexity of each item.
Unrealistic item sizes set by the Product Owner can have negative consequences, such as:
- Difficulty in estimating and planning work.
- Overwhelmed Development Team leading to reduced productivity.
- Scope creep and potential delays in delivery.
Development Team’s Responsibilities
The Development Team provides input on item sizing based on their technical expertise and understanding of the project’s scope. They consider factors such as:
- The complexity of the item’s implementation.
- The availability of resources and dependencies.
- The potential risks and uncertainties associated with the item.
Collaboration between the Product Owner and Development Team is crucial to ensure that item sizes are aligned with the team’s capabilities and the project’s objectives.
Scrum Master’s Responsibilities
The Scrum Master facilitates the backlog item sizing process by:
- Guiding discussions between the Product Owner and Development Team.
- Encouraging consensus and ensuring that all perspectives are considered.
- Providing training and support on estimation techniques.
Having a Scrum Master involved in sizing activities brings several benefits:
- Improved communication and collaboration within the team.
- Increased transparency and understanding of item complexity.
- Reduced risk of unrealistic item sizes and potential delays.
Best Practices for Backlog Item Sizing
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Story Points | Easy to understand, allows for relative estimation. | Subjective, can lead to variations in interpretation. | 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40, 100 |
| Ideal Days | Focuses on effort rather than complexity. | Requires accurate time tracking, can be influenced by external factors. | 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40 |
| T-shirt Sizing | Quick and informal, useful for high-level estimation. | Very subjective, provides limited detail. | XS, S, M, L, XL, XXL |
| Pitfall | Solution |
|---|---|
| Over-estimation | Break down items into smaller chunks, seek input from the Development Team. |
| Under-estimation | Consider all aspects of the item’s implementation, consult with the Development Team. |
| Inconsistent sizing | Establish clear guidelines and use a consistent estimation technique. |
Tools and Techniques for Backlog Item Sizing
| Tool/Technique | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning Poker | Team-based estimation technique using cards with story points. | Encourages collaboration, reduces bias. | Can be time-consuming, requires training. |
| Affinity Mapping | Grouping related backlog items to identify patterns and dependencies. | Facilitates understanding of item complexity, improves collaboration. | Can be difficult to manage large numbers of items. |
| Estimation Poker Online | Virtual version of Planning Poker using online tools. | Convenient, allows for remote estimation. | May lack the same level of interaction as in-person sessions. |
Case Study: Example of Backlog Item Sizing in Practice
In a software development project, the Product Owner and Development Team struggled to agree on the size of a complex feature. The Product Owner initially estimated it as a 5-story point item, while the Development Team argued for a 13-story point estimate.
To resolve the issue, the Scrum Master facilitated a sizing session using Planning Poker. The team discussed the item’s dependencies, potential risks, and implementation details. After several rounds of estimation, they reached a consensus on a size of 8 story points.
This process helped align the team’s expectations, improved communication, and ensured that the item was appropriately sized for the project’s scope and timeline.
FAQ Section
Who is primarily responsible for determining product backlog item size?
The Product Owner holds the primary responsibility for defining the size of product backlog items.
What factors should the Development Team consider when estimating item size?
The Development Team should assess factors such as technical complexity, dependencies, and team capacity when estimating item size.
How can the Scrum Master facilitate effective backlog item sizing?
The Scrum Master can guide discussions, foster collaboration between the Product Owner and Development Team, and ensure adherence to best practices.