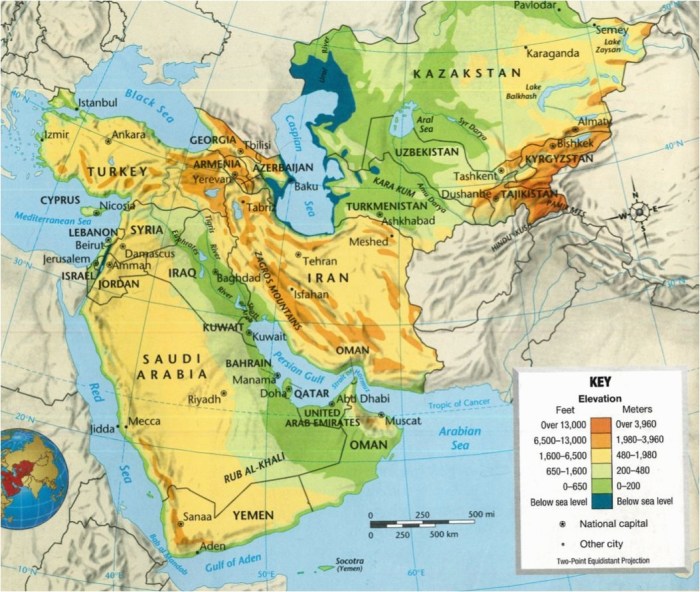
Introducing the comprehensive Southwest Asia Physical Map Labeled, an authoritative resource that unveils the region’s intricate geographic tapestry. This meticulously crafted map not only pinpoints major landmarks but also provides a profound understanding of the physical characteristics that have shaped Southwest Asia’s history, culture, and geopolitical landscape.
Delving into the region’s diverse topography, the map meticulously delineates mountain ranges, rivers, water bodies, deserts, and other arid landscapes. Each feature is meticulously labeled, offering a comprehensive guide to the region’s physical geography.
Geographic Features
Southwest Asia exhibits a diverse array of geographic features, including towering mountain ranges, vast deserts, and significant rivers and water bodies.
Mountain Ranges
The region is home to several prominent mountain ranges that shape its landscape and influence its climate. The Zagros Mountains stretch along the western border of Iran, forming a formidable barrier between the Iranian Plateau and the Mesopotamian Plain. To the north, the Caucasus Mountains form a natural boundary between Europe and Asia, while the Alborz Mountains run parallel to the southern coast of the Caspian Sea.
The Hindu Kush Mountains dominate the eastern part of the region, extending from Afghanistan into Pakistan and providing a natural barrier between Central and South Asia.
Rivers and Water Bodies
Southwest Asia is characterized by several significant rivers and water bodies. The Tigris and Euphrates rivers originate in Turkey and flow through Iraq, forming the fertile Mesopotamian Plain. The Jordan River flows into the Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth’s surface.
The Persian Gulf, an extension of the Indian Ocean, separates the Arabian Peninsula from Iran and Iraq. The Caspian Sea, the largest inland sea in the world, lies to the north of Iran.
Deserts and Arid Landscapes
A significant portion of Southwest Asia is covered by deserts and other arid landscapes. The Arabian Desert, one of the largest deserts in the world, covers much of the Arabian Peninsula. The Karakum Desert in Turkmenistan and the Lut Desert in Iran are also notable examples.
These deserts are characterized by extreme temperatures, limited precipitation, and sparse vegetation. The presence of these arid regions has had a profound impact on the human geography and economic development of the region.
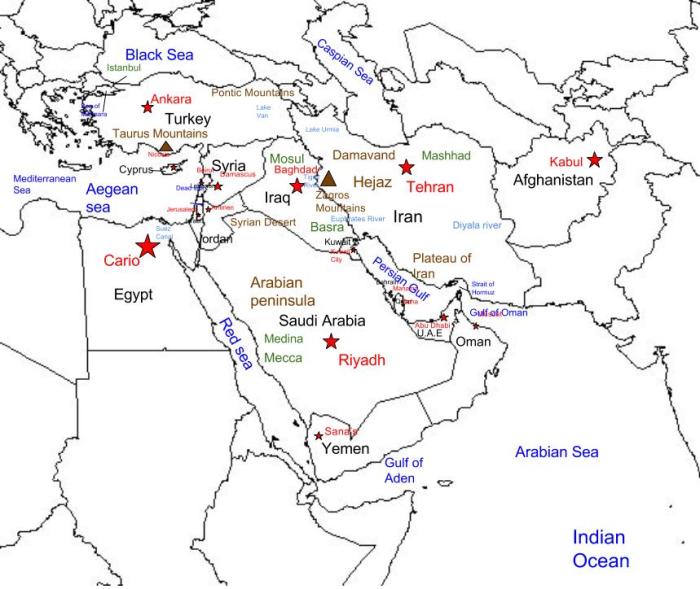
Political Boundaries: Southwest Asia Physical Map Labeled
Southwest Asia, also known as the Middle East, is a politically complex region with numerous countries and borders. The region has a long history of territorial disputes and border conflicts, which continue to shape its political landscape.
The following table provides an overview of the countries located in Southwest Asia, along with their capital cities, populations, and political systems:
Countries of Southwest Asia, Southwest asia physical map labeled
| Country | Capital City | Population (est.) | Political System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bahrain | Manama | 1.7 million | Constitutional monarchy |
| Cyprus | Nicosia | 1.2 million | Presidential republic |
| Egypt | Cairo | 102 million | Semi-presidential republic |
| Iran | Tehran | 84 million | Islamic republic |
| Iraq | Baghdad | 40 million | Federal parliamentary republic |
| Israel | Jerusalem | 9.2 million | Parliamentary democracy |
| Jordan | Amman | 10 million | Constitutional monarchy |
| Kuwait | Kuwait City | 4.6 million | Constitutional monarchy |
| Lebanon | Beirut | 6.8 million | Parliamentary republic |
| Oman | Muscat | 5.1 million | Absolute monarchy |
| Palestine | Ramallah (de facto) | 5.1 million | Semi-presidential republic |
| Qatar | Doha | 2.9 million | Constitutional monarchy |
| Saudi Arabia | Riyadh | 35 million | Absolute monarchy |
| Syria | Damascus | 17 million | Presidential republic |
| Turkey | Ankara | 84 million | Presidential republic |
| United Arab Emirates | Abu Dhabi | 9.9 million | Federal monarchy |
| Yemen | Sana’a | 29 million | Presidential republic |
Territorial disputes and border conflicts have been a major source of instability in Southwest Asia. Some of the most significant conflicts include:
- The Arab-Israeli conflict, which has been ongoing since the 1940s and has resulted in several wars and ongoing tensions.
- The Iran-Iraq War, which lasted from 1980 to 1988 and resulted in hundreds of thousands of casualties.
- The Gulf War, which began in 1990 with the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait and ended with the defeat of Iraq by a US-led coalition.
- The Syrian Civil War, which began in 2011 and has resulted in a humanitarian crisis and the displacement of millions of people.
These conflicts have had a profound impact on the region and continue to shape its political landscape.
Climate and Vegetation
Southwest Asia encompasses diverse climate zones that significantly influence the region’s vegetation. These climate zones range from arid deserts to temperate forests, shaping the distribution of plant and animal species.
Arid and Semi-Arid Climate
Vast areas of Southwest Asia experience arid and semi-arid climates, characterized by low precipitation and high temperatures. The Arabian Desert, for instance, receives less than 100 millimeters of annual rainfall, resulting in sparse vegetation. Desert plants have adapted to these harsh conditions, exhibiting features such as thick cuticles, reduced leaf size, and deep root systems to access groundwater.
Mediterranean Climate
The Mediterranean climate zone extends along the southern and eastern coasts of Southwest Asia, receiving moderate rainfall during winter and hot, dry summers. This climate supports a rich diversity of vegetation, including evergreen forests of oak, pine, and olive trees.
The region’s coastal areas are also home to a variety of shrubs and wildflowers.
Temperate Climate
In the northern and mountainous regions of Southwest Asia, temperate climates prevail. These areas experience colder winters and milder summers, with ample precipitation. Temperate forests of beech, maple, and spruce trees dominate the landscape, providing habitats for a wide range of animal species.
Challenges and Opportunities
The region’s diverse climate and vegetation present both challenges and opportunities. Arid conditions in some areas pose challenges for agriculture and water availability, while temperate regions offer favorable conditions for forestry and tourism. The region’s rich biodiversity provides valuable ecosystem services, such as carbon sequestration and soil conservation.
Natural Resources
Southwest Asia possesses a wealth of natural resources, including oil, natural gas, minerals, and water. These resources have played a significant role in shaping the region’s economic and political landscape.
Oil and Natural Gas
Southwest Asia is home to some of the world’s largest oil and natural gas reserves. The region’s oil production accounts for a significant portion of global supply, and its natural gas reserves are among the largest in the world. The abundance of these resources has fueled economic growth in many countries in the region and has made them major players in the global energy market.
However, the reliance on oil and gas has also created economic and geopolitical challenges. The region has been subject to political instability and conflict due to competition for control of these resources. Additionally, the extraction and use of these resources have contributed to environmental degradation and climate change.
Minerals
Southwest Asia is also rich in a variety of minerals, including copper, gold, silver, and phosphates. These minerals are used in a wide range of industries, from construction to electronics. The mining and export of minerals have been important economic activities in the region for centuries.
However, the mining of minerals can have negative environmental impacts, including air and water pollution, land degradation, and deforestation. It is important to ensure that mining is conducted in a responsible and sustainable manner to minimize these impacts.
Water
Water is a scarce resource in Southwest Asia, and its availability is a major concern for many countries in the region. The region is home to several major rivers, including the Nile, Tigris, and Euphrates, but these rivers are often overused and polluted.
Water scarcity has led to conflicts between countries in the region, and it is a major threat to human health and economic development. It is essential to develop sustainable water management strategies to ensure that water resources are used wisely and equitably.
Cultural Diversity
Southwest Asia is a melting pot of diverse ethnic groups, languages, and religions, reflecting the region’s rich history as a crossroads of civilizations.
This cultural diversity has shaped the region’s history and society, contributing to its vibrant cultural heritage and complex political landscape.
Ethnic Groups
Southwest Asia is home to numerous ethnic groups, including Arabs, Persians, Kurds, Turks, Armenians, and many others. Each group has its own distinct language, customs, and traditions.
Languages
The linguistic landscape of Southwest Asia is equally diverse, with Arabic, Persian, Turkish, and Kurdish being the most widely spoken languages. Other languages, such as Hebrew, Armenian, and Azeri, are also spoken in the region.
Religions
Southwest Asia is a region of diverse religious beliefs, with Islam being the dominant religion. Other religions practiced in the region include Christianity, Judaism, Zoroastrianism, and Baha’i.
Challenges and Opportunities
Cultural diversity presents both challenges and opportunities for Southwest Asia. On the one hand, it can lead to tensions and conflict, as different groups compete for resources and political power. On the other hand, it can also be a source of creativity, innovation, and cultural exchange.
FAQ Explained
What is the significance of the Southwest Asia Physical Map Labeled?
The map provides a comprehensive overview of the region’s physical geography, including mountain ranges, rivers, water bodies, deserts, and other arid landscapes, offering valuable insights into the region’s topography and its impact on human settlement, economic development, and political dynamics.
How does the map contribute to understanding the region’s history and culture?
By pinpointing significant geographical features, the map sheds light on the physical factors that have influenced the development of civilizations, trade routes, and cultural exchanges in Southwest Asia throughout history.
What are the key features highlighted on the map?
The map meticulously labels major mountain ranges, rivers, water bodies, deserts, and other arid landscapes, providing a detailed and accurate representation of the region’s diverse topography.