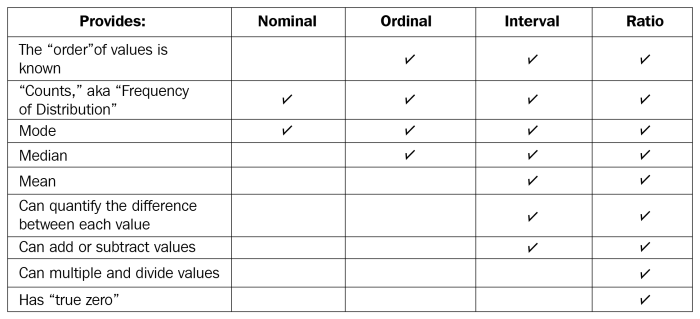
Analyzing numerical data using ratios is a powerful technique that unveils hidden patterns and relationships within complex datasets. Ratios provide a concise and standardized method to compare different data points, enabling us to draw meaningful conclusions and make informed decisions.
Ratios are mathematical expressions that represent the relationship between two or more numerical values. They allow us to compare data across different units of measurement, time periods, or entities, facilitating meaningful comparisons and the identification of trends.
Understanding Numerical Data Ratios
Numerical data ratios are a powerful tool for analyzing and interpreting numerical data. They provide a concise and meaningful way to compare different aspects of data, identify patterns, and make informed decisions.
Ratios are particularly useful when working with large datasets or when comparing data across different time periods or groups. By reducing the data to a single number, ratios allow for easy comparisons and can reveal insights that may not be apparent from the raw data alone.
Types of Numerical Data Ratios, Analyzing numerical data using ratios
- Liquidity ratios:Measure a company’s ability to meet its short-term financial obligations.
- Solvency ratios:Assess a company’s ability to meet its long-term financial obligations.
- Profitability ratios:Evaluate a company’s profitability and efficiency.
- Activity ratios:Measure how efficiently a company is using its assets.
- Market value ratios:Compare a company’s market value to its financial performance.
Calculating Numerical Data Ratios
Calculating numerical data ratios is a straightforward process. The formula for each ratio will vary depending on the type of ratio being calculated.
| Ratio Type | Formula |
|---|---|
| Current ratio | Current assets / Current liabilities |
| Debt-to-equity ratio | Total debt / Total equity |
| Gross profit margin | Gross profit / Revenue |
| Inventory turnover ratio | Cost of goods sold / Average inventory |
| Price-to-earnings ratio | Market value per share / Earnings per share |
Interpreting Numerical Data Ratios
Interpreting numerical data ratios requires an understanding of the industry and context in which the ratios are being used.
- Compare ratios to industry benchmarks:Industry benchmarks provide a reference point for evaluating a company’s performance relative to its peers.
- Track ratios over time:Tracking ratios over time can reveal trends and patterns that may indicate changes in a company’s financial health or performance.
- Consider other financial data:Ratios should not be interpreted in isolation. It is important to consider other financial data, such as financial statements and market conditions, to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial position.
Questions and Answers: Analyzing Numerical Data Using Ratios
What are the benefits of using ratios in data analysis?
Ratios provide a standardized and concise way to compare data, identify trends, and make meaningful comparisons across different units of measurement or time periods.
How do I calculate a ratio?
To calculate a ratio, simply divide one numerical value by another. For example, to calculate the profit margin ratio, divide net profit by total revenue.
What are some common types of ratios?
There are many different types of ratios, including financial ratios, profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, and efficiency ratios. Each type of ratio has a specific purpose and application.